Request a Callback
Clinic Timings
- Mon to Sat 8:00 AM - 8:00 PM
- Sunday Closed
Contact Us
Address -
Ground Floor, Manoj Cooperative Housing Society, Shankar Ghanekar Marg, Prabhadevi, Mumbai- 400025
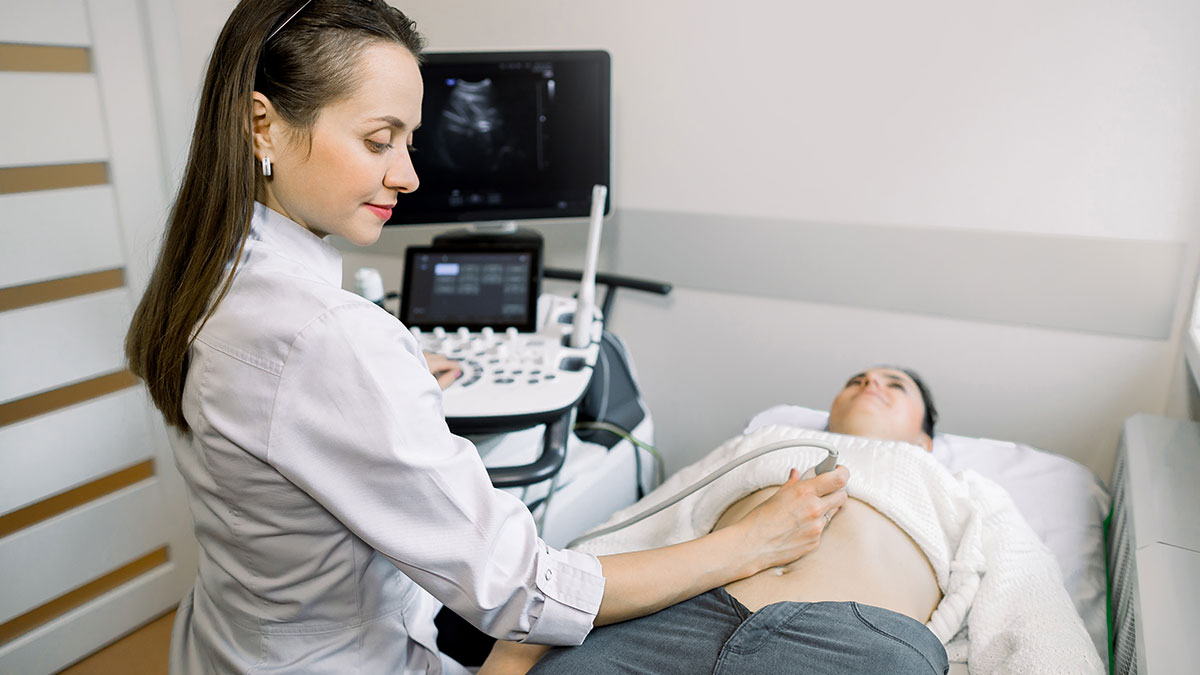
What is Ultrasound?
Ultrasound test, also known as USG, sonography test or ultrasonography test, is a non-invasive, painless and radiation free mode of imaging technique used to assess various abdominal and pelvic organs, vascular structure, muscles and tendons. It is also performed to evaluate any congenital abnormalities, well-being and optimal growth of a foetus during pregnancy.
Ultrasound for pregnancy or USG for pregnancy is a primary mode of diagnostic imaging technique to provide diagnosis during pregnancy.
With the advances in ultrasound technology, we can obtain 3D ultrasound and 4D ultrasound images of the foetus, know the architecture of the liver using shear wave technique and demarcate the lesions in thyroid and breast by elastography.
What is 3D Ultrasound/4D Ultrasound?
A three-dimensional i.e.3D ultrasound is one of the most advanced techniques of ultrasound in which a standard, two-dimensional greyscale ultrasound image is converted into a volumetric, three-dimensional image.
With the help of post-processing techniques and AI (artificial intelligence), the acquired image is enhanced and can be viewed in all the three-axis for a detailed examination. This technique has been developed in order to solve issues related to obstetrics and gynaecology thereby reducing the dependence on ultrasonography test and also avoid operator related insufficiencies.
A four-dimensional i.e. 4D ultrasound is a real-time, dynamic ultrasound that complements 2D and 3D examination. By use of 4D ultrasound, the medical practitioner can assess dynamic images of the foetal face, respiratory movements, swallowing, movements of the lips and mouth, blinking of eyes and limbs movements.
A 3D ultrasound can be useful in gynaecology for the detection of uterine anomalies such as Mullerian duct abnormalities, to check the position of the intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD), to locate and characterize uterine fibroid, endometrial polyps. It may also be useful in imaging adnexal lesions such as cysts, exophytic fibroids etc.
Why is Sonography Test/Ultrasound Test performed?
- Whole abdomen ultrasound is performed to diagnose pathologies like appendicitis, liver/ spleen enlargement, various hernias, bowel obstruction.
- To diagnose pathologies of pelvis in females like fibroids, ovarian cysts, PCOD.
- To diagnose pathologies of pelvis in males like prostatomegaly (BPH).
- To diagnose pathologies of kidneys such as cysts, mass lesions, calculi, urinary tract infection.
- For follicular monitoring.
- To diagnose pregnancy, know number of foetuses, detection of congenital foetal abnormalities.
- Colour Doppler study to evaluate foetal blood flow, Doppler ultrasound studies of arteries and veins to see for varicose veins, peripheral vascular disease.
- To perform Renal Doppler, Carotid Doppler, Portal Doppler and Scrotal Doppler.
At Sirona Diagnostics, we offer a wide range of sonography tests:
- USG Abdomen and Pelvis: A whole abdomen ultrasound and pelvis ultrasound to look for pathologies of liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, both kidneys, urinary bladder, prostate in male while uterus and ovaries in the females.
- USG Breast (Sono-Mammography): A detailed ultrasound to look for pathologies of bilateral breasts, nipple-areola complexes and bilateral axillae.
- USG KUB (Kidney-ureter-bladder): A detailed ultrasound to look for pathologies of both kidneys, urinary bladder, ureters and prostate in male.
- USG Scrotum (Testes): A detailed ultrasound to look for pathologies of both testes, inguinal region, epididymis and to look for varicocele.
- USG Colour Doppler of Peripheral limbs (Arterial Doppler / Venous Doppler): A detailed ultrasound to look for arterial or venous insufficiencies of peripheral limb vessels, deep venous thrombosis, PIVD, varicose veins, arterial occlusion and diabetic neuropathy.
- USG B-Scan: A detailed ultrasound to look for pathologies of the orbit such as cataract, vitreous hemorrhage, retinal detachment and foreign body impaction.
- USG Neck: A detailed ultrasound to look for pathologies of the thyroid gland, parotid glands and submandibular and also to look for pathologies of lymph node.
- USG Chest: A detailed ultrasound of the chest to look for diaphragmatic movements, pleural pathologies, and pneumothorax.
- USG Inguinal Region: A detailed ultrasound of the inguinal region to look for hernia, lymphadenopathy or other mass lesions.
How is the Ultrasound Test or Sonography Test conducted?
The patient is usually in supine position with part to be examined exposed. A special water-based gel heated to room temperature is applied to investigate the sound vibrations with a transducer. The radiologist uses the transducer across the part to be examined. The gel assists in getting perspectives on the desired tissues, and constructions. The gel is later wiped off after the test.
The entire procedure takes approximately 15 minutes to 1 hour, depending on the test. Once the test is complete, the high-quality images derived, printed on a glossy paper are used to analyse the results, which are later handed to the patient.
What are the preparations required for Ultrasonography Test?
- Patients are advised to remove jewellery, belts etc which may hinder the part to be examined
- Scans such of whole abdomen ultrasound, kidneys require fasting of about 4-6hrs
- Nothing in particular is required for 3D sonography or 4D sonography scans
- The patient is advised to carry previous reports for comparison




